Breast Feeding – Advantages, Do’s and Dont’s

World Breastfeeding Week (1st August – 7th August) is a time to reinforce the importance of breastfeeding, do’s and don’ts to observe, and much more. This article touches upon some of these aspects, especially for doctors to keep in mind in case of new mothers:
Do's
Propagate exclusive breast feeding for the first 6 months to all pregnant women.
- Breast feeding must be started within 1 hour of birth, with no pre-lacteal feeds such as water, honey etc.
- Mothers must practise exclusive breast feeding from birth up to 6 months of age.
- Introduce appropriate complementary feeding after 6 months of age to all babies even if they are gaining good weight.
Emphasise benefits of breastfeeding to the mother.
- Breastfeeding ensures intake of colostrum, which is full of antibodies.
- Provides optimal nutrition and immuno-protection.
- No water supplementation is required (even in the hottest weather). A simple test for this: If the baby passes urine about 8 to 9 times in 24 hours, the breastfeeding is adequate and NO WATER is needed.
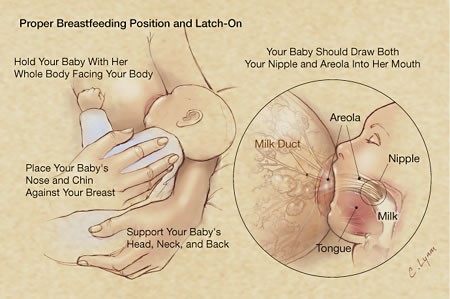
Describe position and latching-on in detail.
Positioning:
- The baby’s head and body should be straight.
- His face should face the breast, with his nose opposite the nipple.
- His mother should hold his body close to hers.
- If the baby is a newborn, she should support his whole body, and not just his head and shoulders
Latching on: Signs of good attachment
- The baby’s chin is touching the breast.
- His mouth is wide open
- His lower lip is turned outwards.
- More areola is visible above the baby’s mouth than below it.
- He takes slow, deep sucks, in bursts with pauses.
REMEMBER IT IS “BREAST FEEDING & NOT NIPPLE FEEDING”
Don'ts
Do not interpret crying as always inadequacy of breast feeding:
- Babies do not cry just out of hunger. It can be discomfort, colic, needing closeness hence to be carried.
- Rule out other causes such as illness, blocked nose, sore mouth, pain on bruise following instrumental delivery.
- Give practical help to show ways to comfort crying baby, ways to hold and carry the baby, bring up baby’s wind etc.
Do not state that breast milk is not enough so solids are to be introduced within 6 months:
- Supplementary foods can be given after 4-6 months for the growing needs of the baby but no bottles are necessary at any age. Emphasis should be on fruits. Whenever possible, continue breast feeding as it plays an important role in the child’s second year of life.
Do not endorse wrong & harmful practices in maternity wards:
- Separation of mothers and babies
- Restriction on duration and frequency of breast feeds
- Giving babies routine supplements of water or formula
- Giving mothers free samples of formula to take home.
Do not underestimate possibility of exclusive breast feeding in Twins.
Do not stop breast feeding for minor illnesses of mother.
- Infections such as common cold, upper respiratory tract infections, gastroenteritis etc. are neither life threatening nor are contraindications for breast feeding. These infections are more self limiting and allows protection through antibodies by continously breast feeding. This will help to reduce the possibilities of the infant being infected and exposed to illness.
Do not stop breast feeding if mother is started on medications unless specified by prescribing Physician.
- Most drugs pass into breast milk.
- But almost all medications appear in only small amounts in human milk, usually less than 1% of maternal dosage.
- Very few drugs are contraindicated for breast feeding.
Do not start bottle feeding under any circumstances.
- Occasionally, top feed may be needed to be started for various reasons such as working mother etc.
- Always give the feed either expressed breast milk or top feed with spoon as bottle feeding causes “Nipple confusion”.
- Many problems of artificial feeding especially of infections are due to improper sterilisation of bottles and nipples.
Advantages of breastfeeding to the baby
- Reduces risk of various infectious and non infectious diseases (immunity from mother)
- Better intelligence.
- Better visual maturation.
- Better language development.
- Fewer emotional or behaviour problems.
- Less aggressive personality.
- Fewer minor neurological problems.
Advantages of breastfeeding to the mother
- Promotes emotional bond development of mother and child very strongly.
- Prevents breast problems in mother.
- Reduces risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Reduces Fe-deficiency anemia in mother
- Helps in birth spacing.
Disadvantages of artifical feeding
IMMEDIATE
- Additional expenditure, prone to infections and infestations, high solute load inappropriate for preterm and infants with renal problems, increased incidence of allergies, diabetes, necrotising enterocolitis, hypocalcemic convulsions.
LONG TERM
- Hypertension, Coronary artery and Cerebrovascular diseases, Dyslexia, Multiple Sclerosis and Schizophrenia.
Contraindications
Breastfeeding may not be advised in the following circumstances.
ABSOLUTE
- Galactosemia and congenital lactose intolerance, mothers on cancer chemotherapy, some antithyroid drugs and antipsychotic drugs like lithium.
RELATIVE
- HIV (as in developing countries, advantages of breast feeding outweigh the risk of transmission of HIV through breast feeding).

By Dr. Deepali Prabhat
MBBS, MD, DGO. DFP, DNB -- Consultant Gynaecologist at GSBS Medical Trust.
